厦门大学电子科学与技术学院电子工程系,福建 厦门 361005
为了提升MoS2可饱和吸收体在脉冲激光器中的稳定性和工作性能,本论文采用氧化石墨烯(GO)作为胶体表面活性剂,通过LPE 的方法剥离出少层MoS2,并进一步开展了少层GO-MoS2用于掺铒光纤激光器(EDFL)锁模的实验研究。在实验中获得了中心波长为1558 nm,重复频率为7.86 MHz,脉宽为1.9 ps 的稳定锁模脉冲激光。当泵浦功率为60.5 mW 时,输出功率为0.48 mW,脉冲峰值功率为32.1 W。研究证明,采用这种方法制备的新型复合二维材料有利于保持少层MoS2的稳定性,并且能提高MoS2可饱和吸收体的损伤阈值,以获取更大脉冲能量的超快激光。
被动锁模 光纤激光器 复合二维材料 passive mode-locking fiber laser composite two-dimensional material GO-MoS2 GO-MoS2

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
Conventional Q-switched fiber lasers operating at multi-longitudinal-mode oscillation usually suffer from self-mode-locking-induced temporal instability, relatively strong noise, and low coherence. Here, we address the challenge through demonstrating, for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, a single-longitudinal-mode (SLM) Er-doped fiber (EDF) laser passively Q-switched by a few-layer Bi2Se3 saturable absorber (SA). The Bi2Se3 SA prepared by the liquid-phase exfoliation method shows a modulation depth of ~5% and saturation optical intensity of 1.8 MW/cm2. A section of 1-m unpumped EDF together with a 0.06-nm-bandwidth fiber Bragg grating is used as an ultra-narrow autotracking filter to realize SLM oscillation. Stable SLM Q-switching operation at 1.55 μm is successfully achieved with the spectral linewidth as narrow as 212 kHz and the pulse duration of 2.54 μs, manifesting near-transform-limited pulses with a time-bandwidth product of 0.53. In particular, we found that the SLM Q-switching possesses the higher signal-to-noise ratios of 62 dB (optical) and 48 dB (radio frequency), exhibiting its advantages of low noise and high stability. Such an SLM Q-switched fiber laser could gain great interest for some applications in coherent detection, coherent optical communications, and high-sensitivity optical sensing.
Lasers, fiber Lasers, Q-switched Photonics Research
2018, 6(10): 10000C29
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139, USA
2 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
3 College of Information Science and Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
4 Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Materials and Devices of Zhejiang Province, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
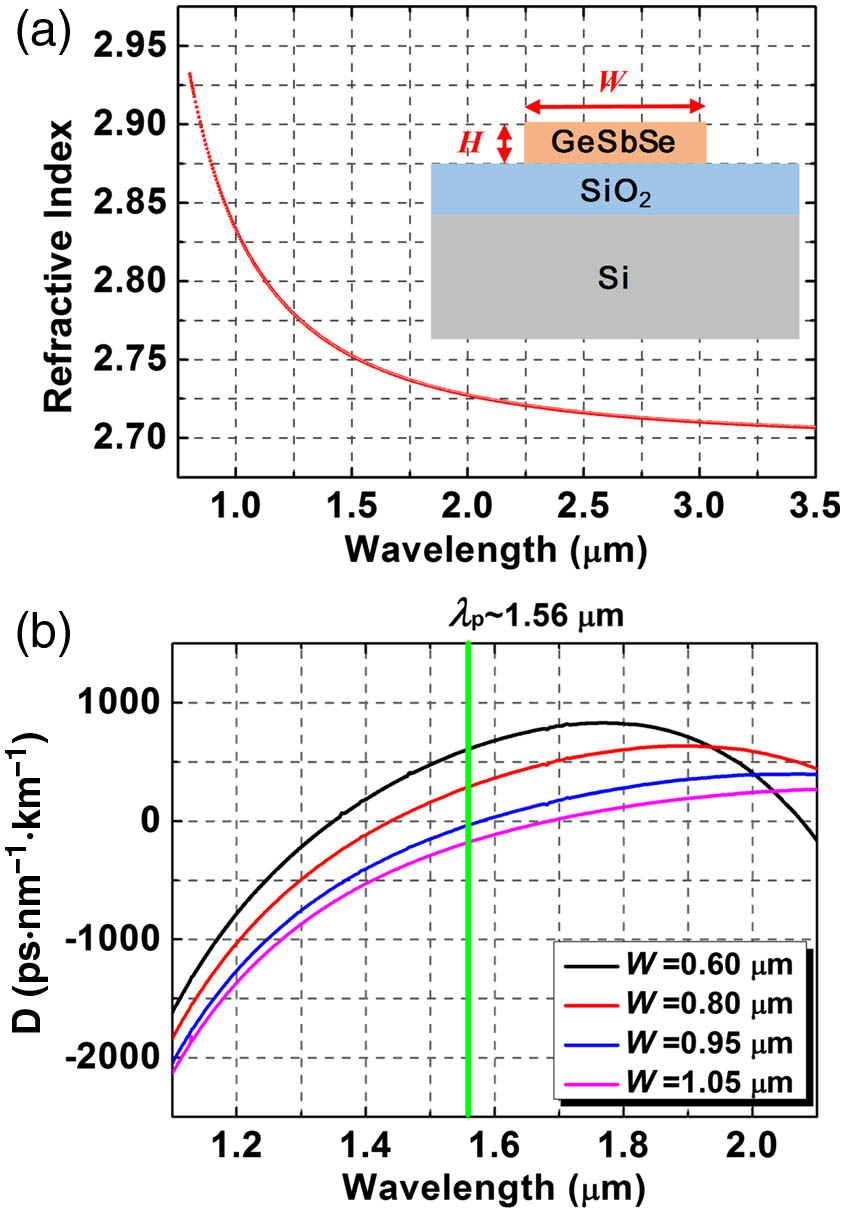
On-chip spectroscopic sensors have attracted increasing attention for portable and field-deployable chemical detection applications. So far, these sensors largely rely on benchtop tunable lasers for spectroscopic interrogation. Large footprint and mechanical fragility of the sources, however, preclude compact sensing system integration. In this paper, we address the challenge through demonstrating, for the first time to our knowledge, a supercontinuum source integrated on-chip spectroscopic sensor, where we leverage nonlinear Ge22Sb18Se60 chalcogenide glass waveguides as a unified platform for both broadband supercontinuum generation and chemical detection. A home-built, palm-sized femtosecond laser centering at 1560 nm wavelength was used as the pumping source. Sensing capability of the system was validated through quantifying the optical absorption of chloroform solutions at 1695 nm. This work represents an important step towards realizing a miniaturized spectroscopic sensing system based on photonic chips.
Sensors Supercontinuum generation Photonics Research
2018, 6(6): 06000506
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Department of Biomaterials, College of Materials, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
3 e-mail: jweng@xmu.edu.cn
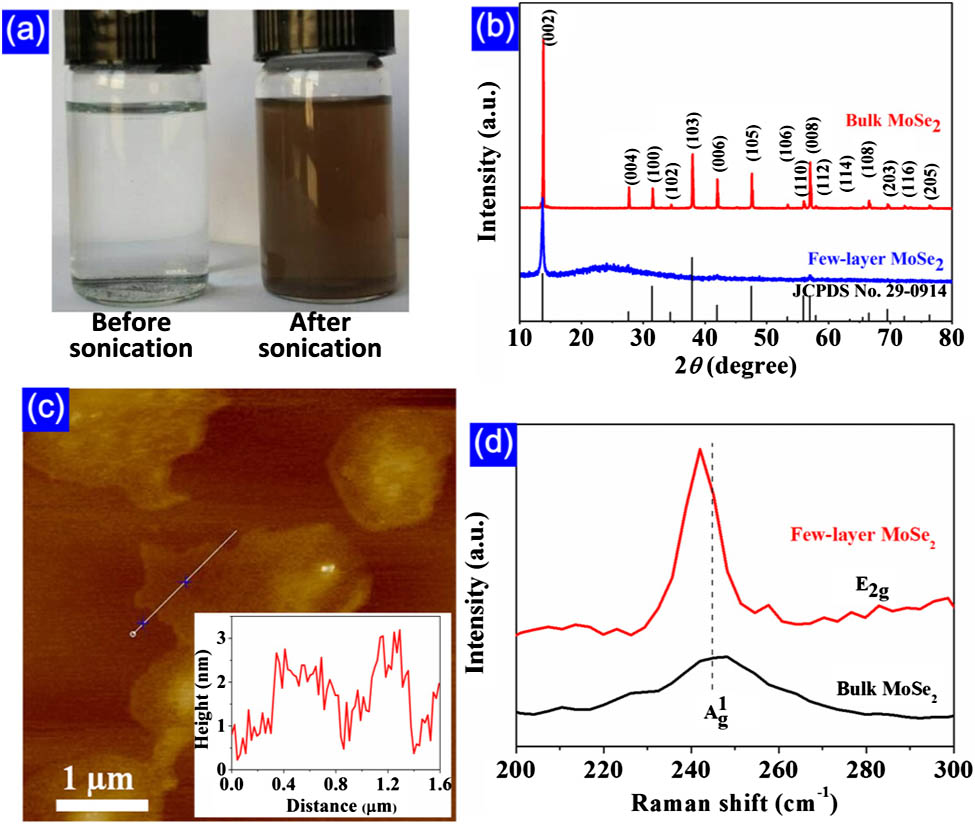
In this paper, both nonlinear saturable absorption and two-photon absorption (TPA) of few-layer molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2) were observed at 1.56 μm wavelength and further applied to mode-locked ultrafast fiber laser for the first time to our knowledge. Few-layer MoSe2 nanosheets were prepared by liquid-phase exfoliation method and characterized by x ray diffractometer, Raman spectroscopy, and atomic force microscopy. The obtained few-layer MoSe2 dispersion is further composited with a polymer material for convenient fabrication of MoSe2 thin films. Then, we investigated the nonlinear optical (NLO) absorption property of the few-layer MoSe2 film using a balanced twin-detector measurement technique. Both the saturable absorption and TPA effects of the few-layer MoSe2 film were found by increasing the input optical intensity. The saturable absorption shows a modulation depth of 0.63% and a low nonsaturable loss of ~3.5%, corresponding to the relative modulation depth of 18%. The TPA effect occurred when the input optical intensity exceeds ~260 MW/cm2. Furthermore, we experimentally exploit the saturable absorption of few-layer MoSe2 film to mode lock an all-fiber erbium-doped fiber laser. Stable soliton mode locking at 1558 nm center wavelength is achieved with pulse duration of 1.45 ps. It was also observed that the TPA process suppresses the mode-locking operation in the case of higher optical intensity. Our results indicate that layered MoSe2, as another two-dimensional nanomaterial, can provide excellent NLO properties (e.g., saturable absorption and TPA) for potential applications in ultrashort pulse generation and optical limiting.
Nanomaterials Nonlinear optical materials Lasers, fiber Mode-locked lasers Photonics Research
2015, 3(3): 03000A79





